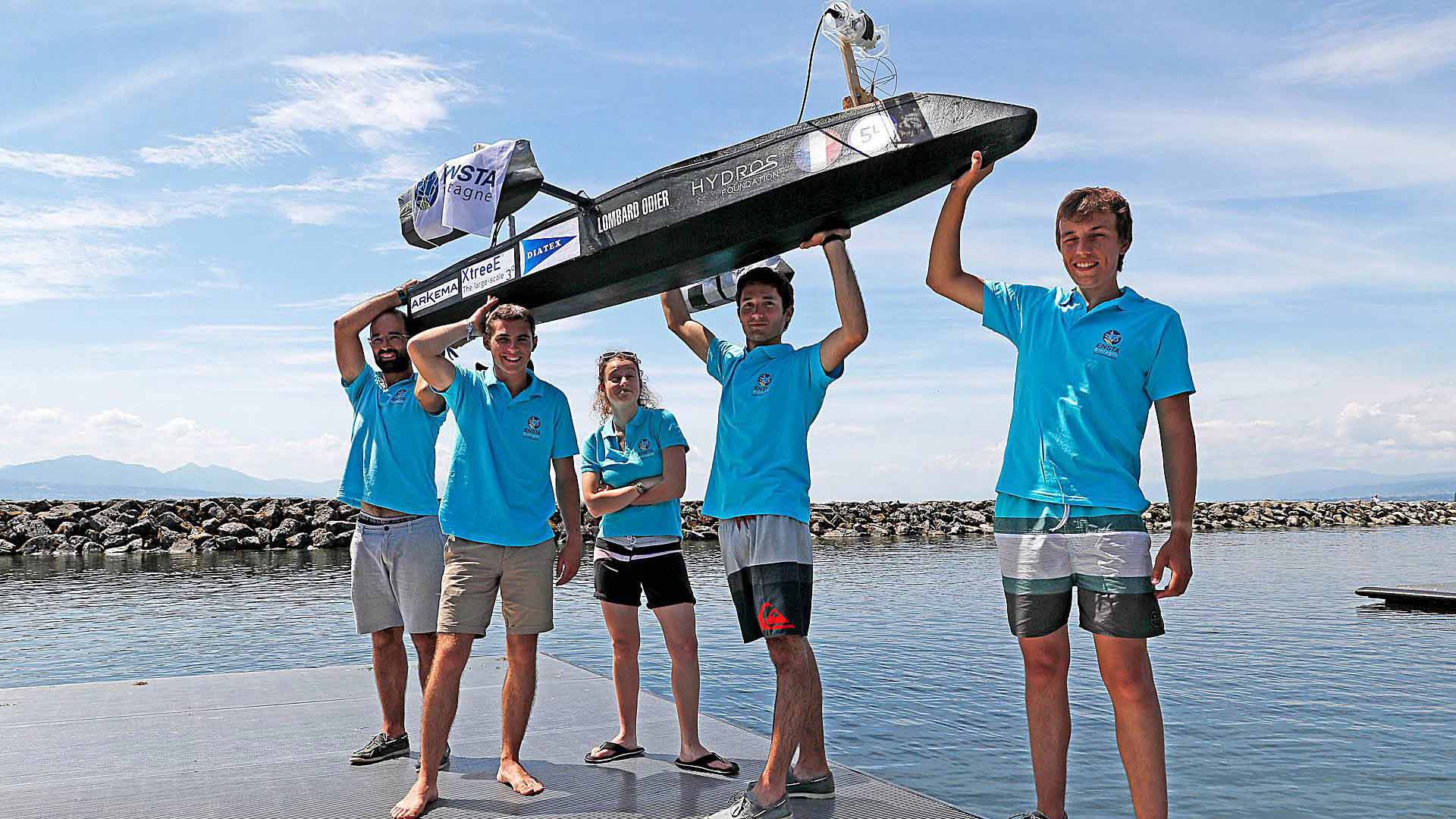
Industry is striving to produce lighter and more fuel-efficient vehicles: cars, planes, ships, commercial vehicles, etc.
ENSTA Bretagne is a partner of choice for determining the service life of these “lightweight” structures, in which, for example, bonded composites replace welded steel.
The in-service performance (sustainability, fatigue) of mechanical systems is one of industry’s major concerns. It is striving, on the one hand, to improve performance and safety, and on the other hand, to reduce maintenance activities, fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. ENSTA Bretagne develops digital predictive models that are experimentally validated using the testing facilities of the MASMECA technology platform.
The use of composites, together with a composite-to-metal bonding technique, boosts the competitiveness of the MRE (marine renewable energy) sector. The challenge is to design systems that can operate durably at sea, with minimal maintenance.
After a research chair and contributions to the development of offshore wind turbines and marine turbines working with Breton SMEs, the work on bonding continues, with the COSICO and INDUSCOL projects backed by the ANR*, France Energies Marines and the Investissements d’Avenir funding program.
A team from ENSTA Bretagne is taking part in numerous international marine environment protection programs using “passive acoustics” technologies. The goal is to be able to process, characterize and analyze underwater sound detected using hydrophones (an efficient, sustainable and non-intrusive method) to better understand marine wildlife and its population movements.
One of the applications is related to the monitoring of marine mammal populations. The team just came back from a research cruise conducted with IUEM in the French Southern and Antarctic Lands. A new project, funded by the TOTAL Foundation, aims to track whales in 3 maritime areas using a glider (autonomous underwater vehicle).
BeyondTheSea® is a project supported by ADEME and the Mer Bretagne Atlantique industry cluster, and led by sailor Yves Parlier.
Towing ships using kites would reduce fuel consumption by 20%. Involved in the project from the start, ENSTA Bretagne is conducting research projects on the kite’s autopilot, a giant kite structure, sail size and the maneuverability and seakeeping ability of the vessel.
For more information: www.beyond-the-sea.com
Département sciences humaines et sociales de l'ENSTA Bretagne, laboratoire Formation et Apprentissages Professionnels.
Ce projet européen soutenu par le fonds européen Erasmus+, rassemble 7 membres et 10 partenaires situés dans 6 pays européens. Il s'intéresse au rôle des ingénieurs dans la société à travers 3 axes :
- Déterminer les futurs rôles et compétences des ingénieurs impliquant une meilleure prise en compte du développement durable.
- Étudiez les valeurs et les motivations des jeunes, des étudiants et des apprenants adultes pour déterminer en quoi ils influencent leurs futurs choix de carrière et utiliser ces connaissances pour rendre le métier d'ingénieur plus attrayant auprès des jeunes.
- Développer de nouvelles pratiques d’enseignement et d’apprentissage innovantes pour répondre à ces résultats.
Plus d'infos : https://www.astep2030.eu/en
Département sciences et technologies de l’information et de la communication ENSTA Bretagne, rattaché au laboratoire Lab-Sticc
L'ENSTA Bretagne est partenaire du projet Méditerranée. Celui-ci vise l'amélioration des modèles météorologiques afin notamment de mieux prévoir les épisodes cévenols (fortes pluies et orages localisés intervenant principalement dans le Sud-Est de la France entraînant des crues exceptionnelles et des inondations).
La thèse en cours vise l’amélioration des méthodes d’analyse des signaux GNSS (GPS, Galileo, Glonass) mesurés par des antennes embarquées en pleine mer (sur des navires ou des bouées scientifiques).

Lighting, heating and insulation
On a daily basis, nearly 1200 people work, study and live on the ENSTA Bretagne campus which spans more than 7 hectares (17.3 acres). With respect to lighting, heating and insulation, investments are made every year to reduce the school’s environmental footprint. Efforts are also made to reduce unnecessary energy consumption (heating, electricity).
Since the summer of 2017, ENSTA Bretagne has been connected to the city’s heating network. 85% of the energy supply comes from household waste incineration. The system significantly limits CO2 emissions into the atmosphere and reduces the school’s reliance on gas.
Parks and gardens maintenance, paper and waste sorting
Brest being located near protected natural areas, the need to stop using chemical fertilizers was self-evident. Chemical fertilizers are no longer used (including for the sports field). They have been replaced by organic compost. The amount of paper used is monitored and comprises 50% recycled materials. Waste sorting is also implemented throughout the campus.
Responsible engineers trained to promote sustainable development
During Year 2, as part of an applied project, all students work on a facility’s carbon footprint. In addition to learning about the Carbon Footprint concept and what it entails, students must evaluate their system’s CO2 emissions and suggest ways to limit its environmental impact.
The Engineering and Business Science major in particular raises awareness of the engineer’s responsibility. This major tackles quality management, ecodesign, etc. It also provides insight into the environment of industrial projects: their social, economic and political context at European and international level, as well as risk analysis.
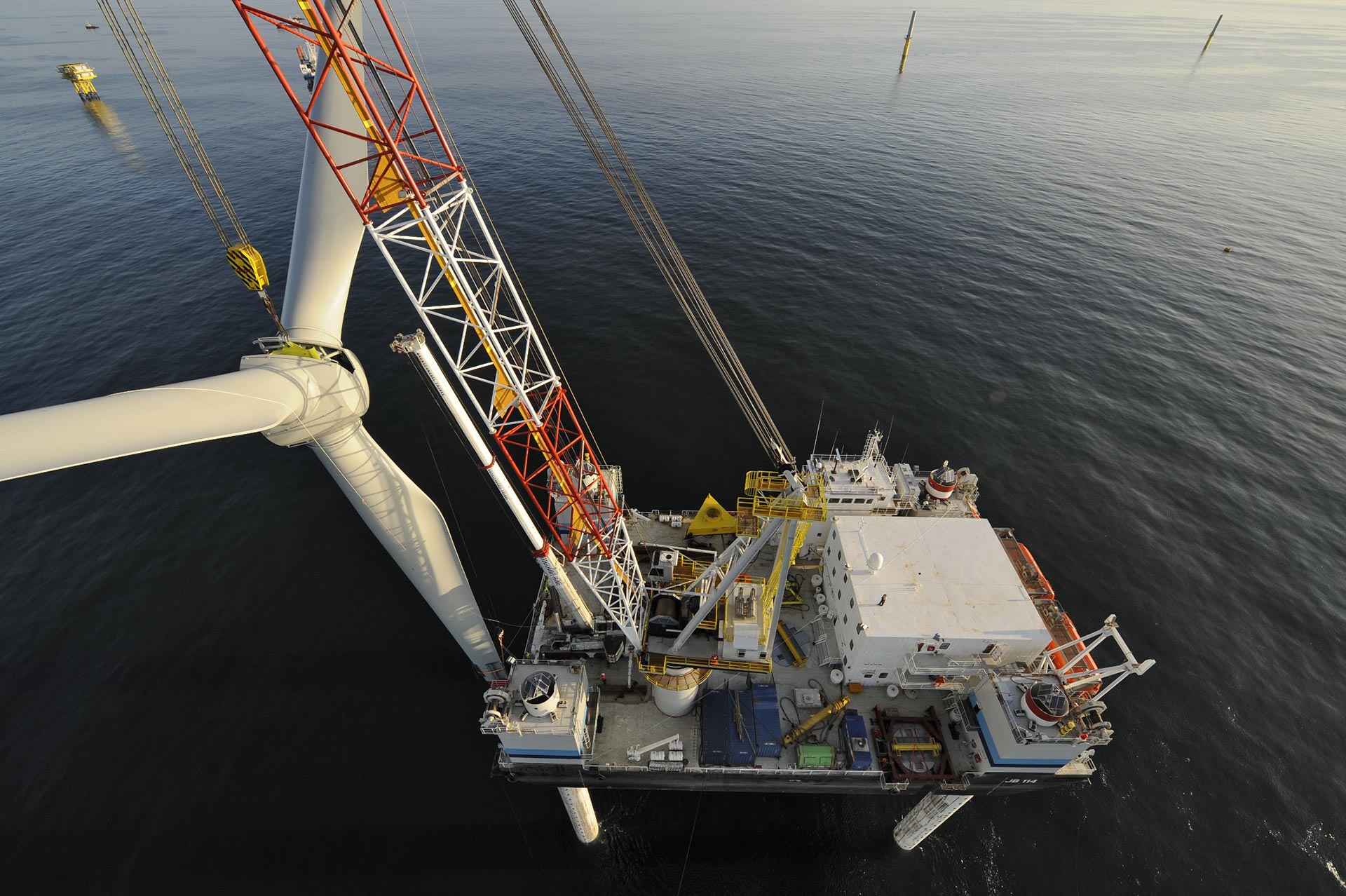

A program focused on the development of marine renewable energy
The Advanced Master in Marine Renewable Energies trains students to become innovative MRE project managers, from the design of high-performance systems for various types of energy resources, to location analysis and environmental and social impact assessment.
Supported by the Mer Bretagne Atlantique industry cluster and the Conférence des Grandes Écoles for nearly 10 years now, this program brings together several higher education institutions based in the Brest area (ENSTA Bretagne, École navale, IMT Atlantique, Université de Bretagne Occidentale/IUEM...) and numerous major organizations and industry players (Ifremer, Naval Group, SHOM, Météo France, Cerema…).
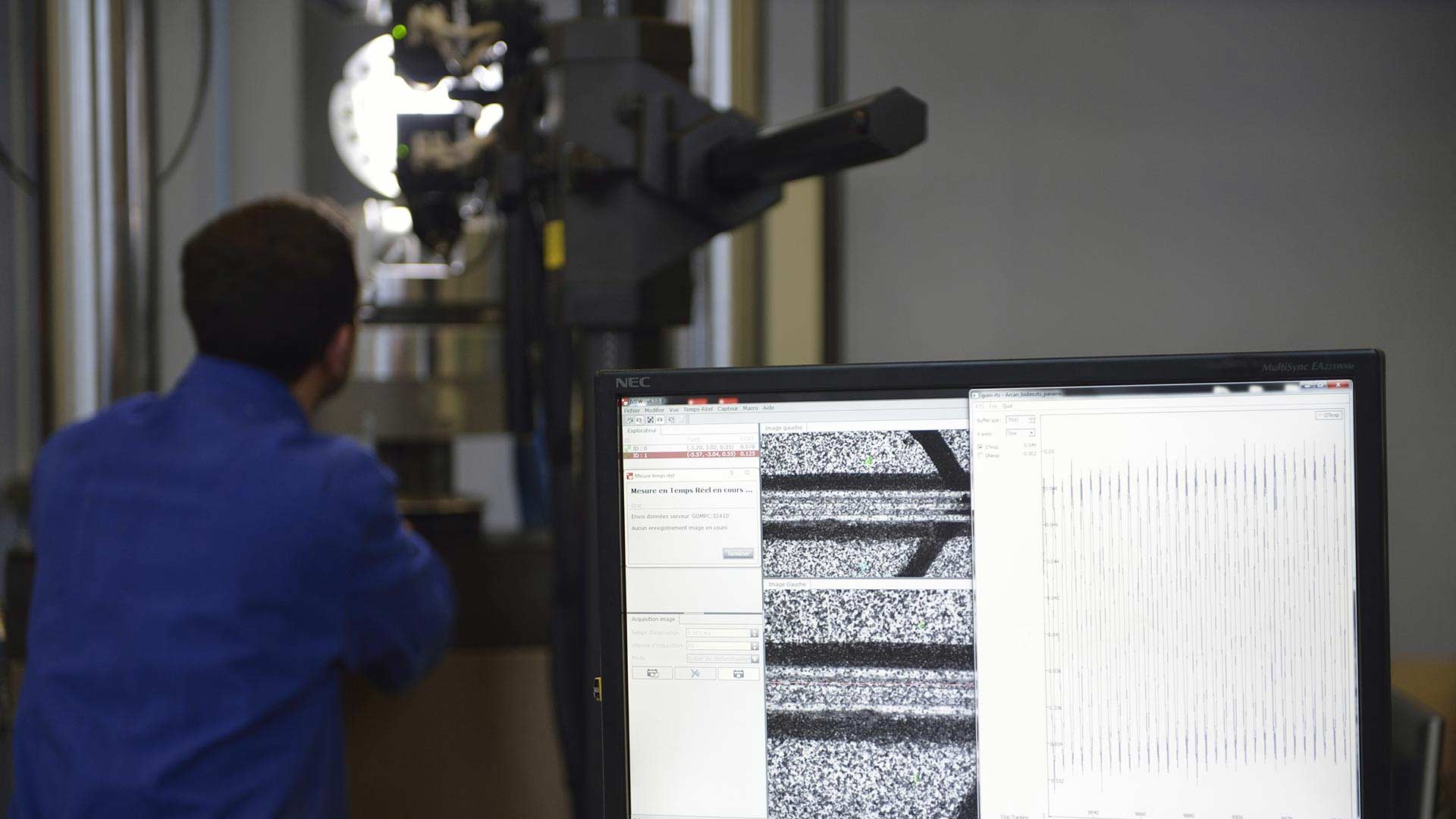

Fuel-efficient transportation systems: predicting the behavior and service life of structures
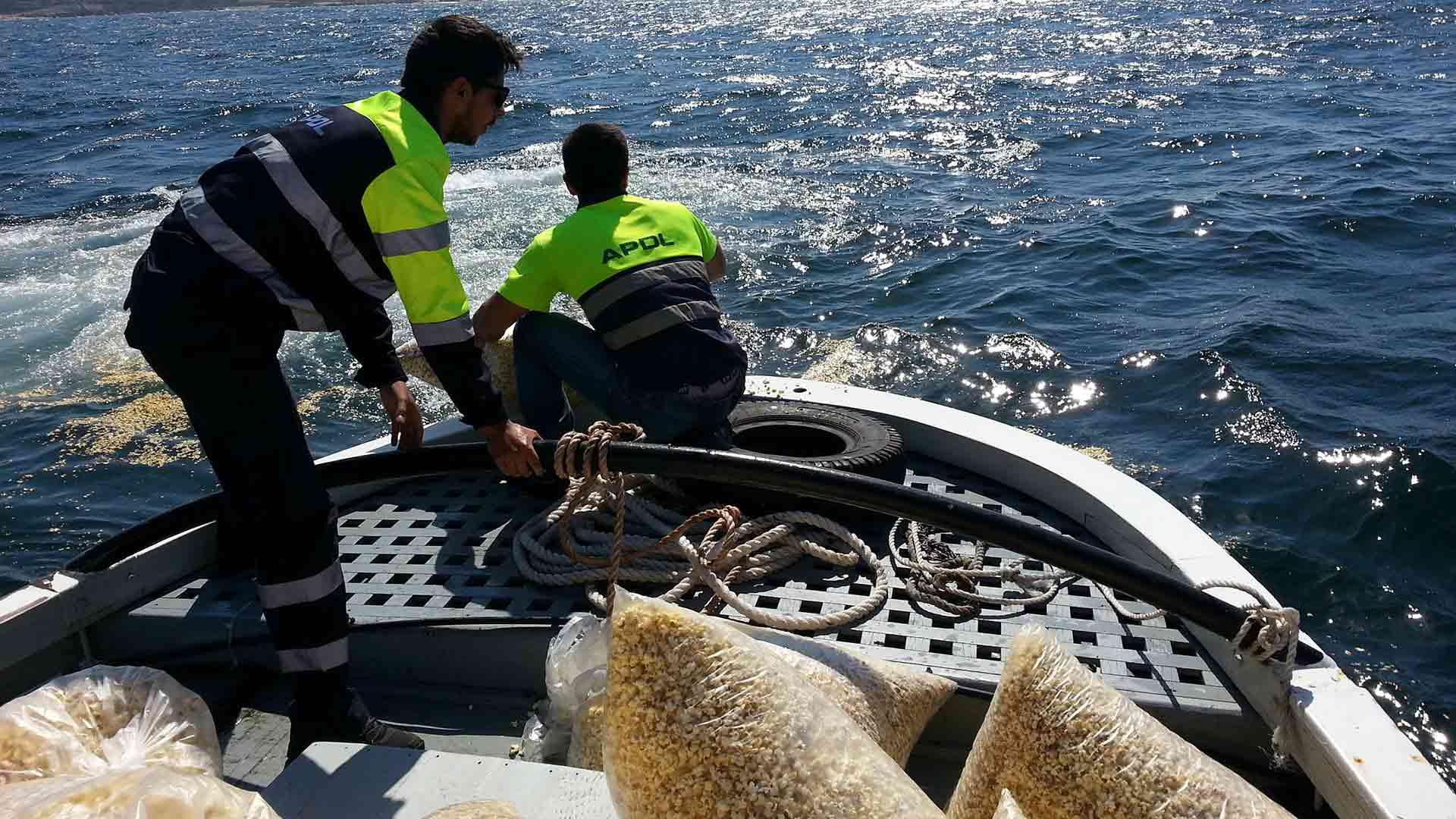

Detecting sea surface pollution: the NETMAR European program
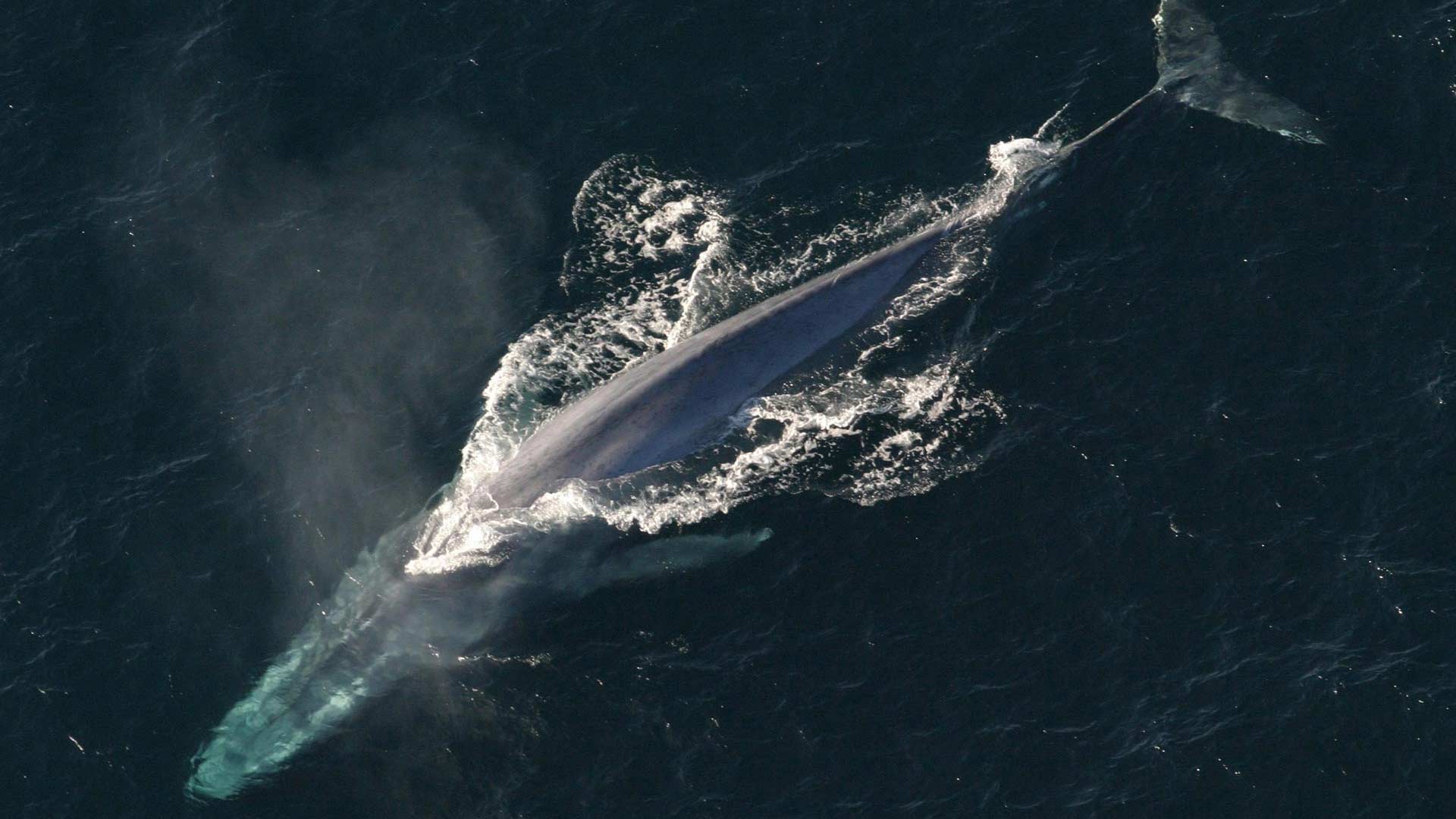

Listening to and counting marine mammals: passive acoustics, an efficient, sustainable and non-intrusive method
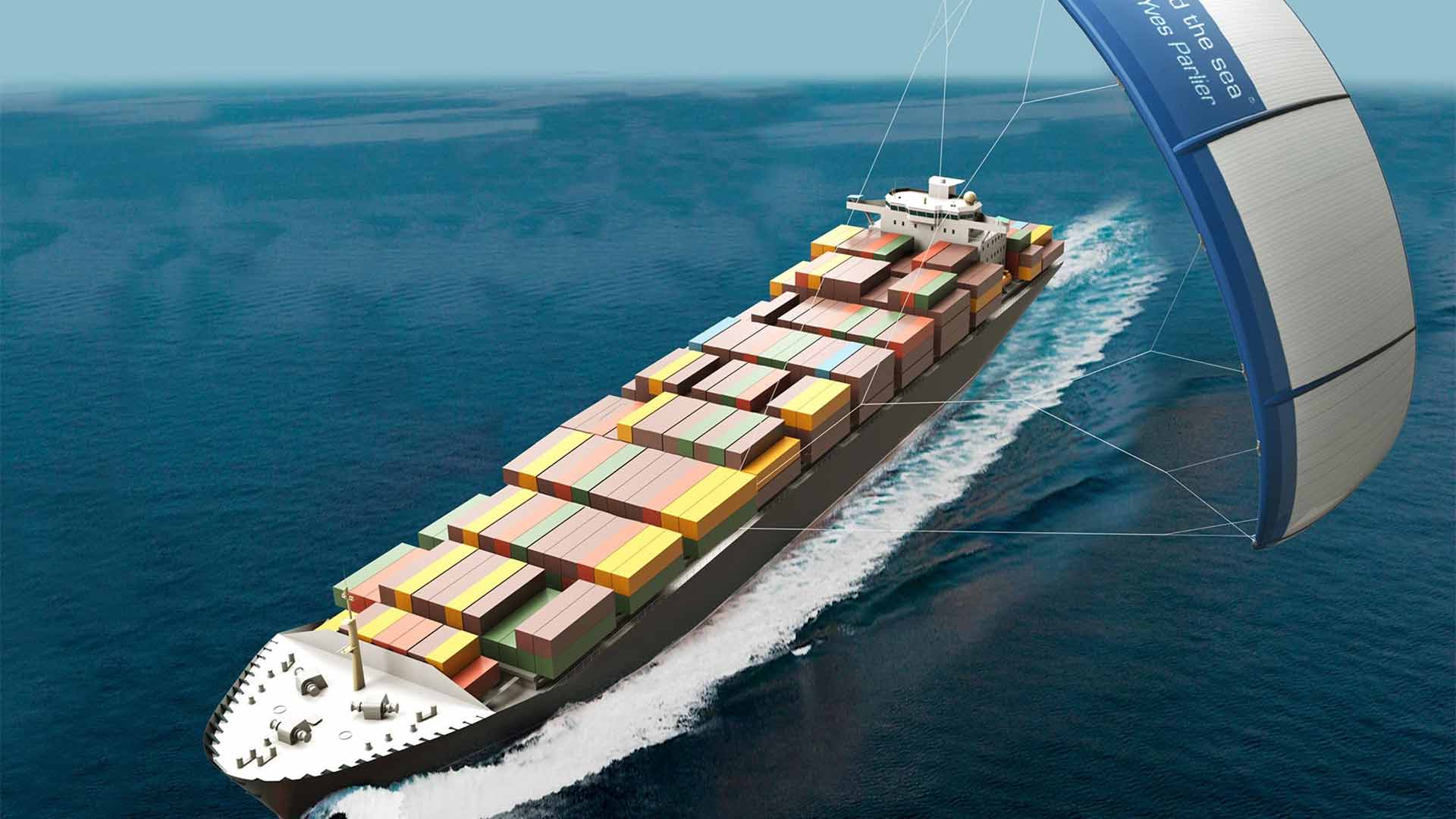

Des navires tractés par des cerfs-volants : ENSTA Bretagne partenaire du projet BeyondThe Sea®
















